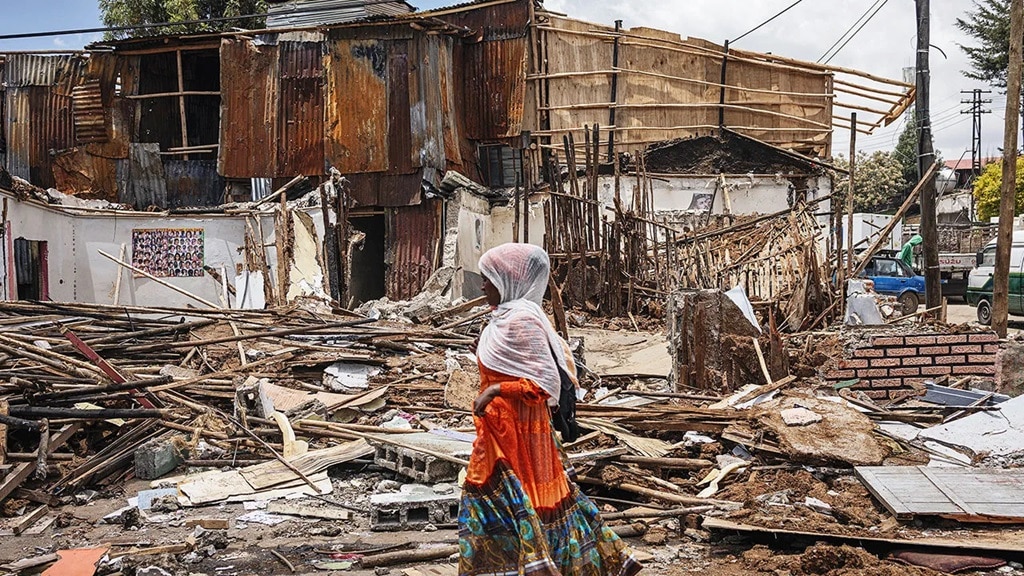
Amnesty International is raising concerns about the ongoing evictions in Ethiopia, urging the authorities to halt these displacements linked to urban development projects. These evictions displace countless families, often with little warning or compensation, and leave them without homes or livelihoods.
Amnesty International is raising concerns about the ongoing evictions in Ethiopia, urging the authorities to halt these displacements linked to urban development projects. These evictions displace countless families, often with little warning or compensation, and leave them without homes or livelihoods.
Urban development is essential, but it must be balanced with the rights and welfare of citizens. Human rights organizations emphasize that any development initiative should prioritize the well-being of communities involved.
Their call to action holds particular importance as Ethiopia continues to grow its cities. Authorities need to engage in more inclusive urban planning, ensuring that all can benefit from modernization.
This attention to fair treatment in the development process is not just relevant in Ethiopia, but serves as a global reminder that progress should be equitable and respectful of human rights.
Overview of Evictions in Ethiopia for Urban Development
The African nation of Ethiopia stands at a crucial crossroads, where thriving urban development is both an opportunity and a challenge. As cities like Addis Ababa expand, they do so with an inherent impact on the communities residing within. Forced evictions have become increasingly common, raising concerns on local and international levels. This overview delves into the context and impacts of these evictions, including economic growth, government policies, and the demographic elements of the affected populations.
Context of Urban Development in Ethiopia
Urban development in Ethiopia is driven by various factors, predominantly by its substantial economic growth. The nation aims to transform its economic landscape by focusing on infrastructure, new buildings, and expanded services. However, this rapid expansion isn’t without consequences.
Economic Growth and Its Impacts
Ethiopia’s economic growth has been noteworthy, driving significant change across its urban areas. This growth has led to increased investments in housing, industry, and transportation infrastructure, promising better living standards and job opportunities. Urban development projects aim to rejuvenate cities, attract foreign investment, and boost the local economy. However, these projects often require land, which inevitably leads to evictions. Many residents, especially those in informal settlements, have faced removal under this growth agenda, often without adequate compensation or resettlement options.
Government Policies on Urban Expansion
Government policies play a critical role in shaping urban development in Ethiopia. The government has instituted plans to improve city landscapes and address housing shortages. Their initiatives focus on creating more organized urban areas, with the formulation of policies that support expansion. Nonetheless, these policies have sometimes led to forced evictions. Critics argue that the process lacks transparency and fails to ensure fair treatment for those displaced. There is a push for policies that are more inclusive and protective of the rights of all residents, especially the vulnerable populations.
Affected Communities and Demographics
Examining who is affected by these urban development policies sheds light on the broader socio-economic patterns at play. Regions facing the most significant changes can offer insight into the intricate web of Ethiopia’s demographic structure.
Regions Facing the Most Evictions
Certain regions in Ethiopia are disproportionately impacted by urban development efforts. Central and densely populated areas, like Addis Ababa, typically see the most substantial evictions due to their high urbanization rates. Other growing cities like Dire Dawa and Mekelle are also experiencing similar patterns. The focus on modernizing central urban areas puts pressure on adjacent zones, displacing communities that have lived there for generations.
Demographic Diversity of Affected Populations
The demographic diversity among the affected populations is vast. Many evicted individuals belong to low-income groups or minority communities. Often residents of informal settlements, these groups face the brunt of urban expansion without robust social safety nets. The resultant displacement may strip them of cultural ties and community networks, further marginalizing them. Understanding these demographic challenges is crucial to creating balanced urban policies that safeguard the interests of all societal segments.
This comprehensive analysis underlines the complex relationship between urban development and community welfare in Ethiopia, urging more inclusive growth strategies that recognize every citizen’s rights.
Amnesty’s Stance and Recommendations
Amnesty’s Concerns Over Forced Evictions
Human Rights Violations Alleged
Amnesty International has expressed grave concerns over the series of forced evictions occurring in Ethiopia, emphasizing the alleged human rights violations. It has been reported that these evictions are often executed with little to no warning, leaving residents in a state of confusion and distress. Inadequate compensation and lack of alternate housing have amplified the allegations of human rights infringements. In some cases, forceful and even violent measures have been used to remove people from their homes, which starkly contrasts with international human rights standards. Amnesty International urges international attention and intervention to prevent further violations and safeguard the dignity of affected citizens.
This is a note about the urgency of addressing human rights violations during evictions.
Social and Economic Consequences
The social and economic consequences of forced evictions in Ethiopia are significant and far-reaching. Displacement from established homes and communities often results in the loss of social networks and economic opportunities. Families uprooted from their homes face difficulties in accessing essential services such as education, healthcare, and employment. The loss of property and economic stability can spiral into extended periods of poverty and hardship. Additionally, the psychological impact of forced relocations cannot be understated, resulting in trauma and prolonged mental health issues for those displaced. Amnesty International highlights these issues as critical areas needing urgent intervention and support to mitigate the negative ripple effects on individuals and communities.
Proposed Solutions by Amnesty
Recommendations for the Ethiopian Government
Amnesty International has outlined several recommendations aimed at the Ethiopian government to remedy the situation of forced evictions. Primarily, the organization urges the government to halt all forced evictions and ensure any necessary evictions comply with international guidelines. There is a call to improve transparency around urban development projects and provide sufficient notice and compensation to those affected. Another recommendation is to facilitate inclusive dialogue among stakeholders, including residents, to ensure fair resettlement processes and safeguard the livelihoods of affected populations. Furthermore, Amnesty stresses the importance of establishing robust legal frameworks to protect residents’ rights against future forced evictions, thereby aligning local laws with global human rights standards.
Calls for International Support and Intervention
In light of the severe impact of forced evictions, Amnesty International is also calling for international support and intervention. The organization seeks to galvanize the global community to hold the Ethiopian government accountable for adhering to human rights commitments. It calls upon international donors and partners to prioritize their assistance towards sustainable and humane urban development initiatives that do not compromise residents’ rights. Amnesty encourages global human rights bodies to monitor the situation and offer technical support to Ethiopian authorities in developing strategic plans that align with international best practices for urban development. Engaging the international community is pivotal in creating a collaborative effort towards ensuring fair treatment and prevention of further displacement of Ethiopian citizens.
Legal Framework Surrounding Evictions
Understanding the legal framework surrounding evictions in Ethiopia provides insight into the national and international obligations that govern how these processes are managed. This includes examining both national laws and urban development policies, as well as aligning these with international human rights standards.
National Laws and Urban Development Policies
Ethiopian laws and policies play a central role in the urban development strategy of the nation. It’s crucial to explore the specific legislations and assess the protections they afford to residents facing eviction.
Key Legislations Impacting Evictions
Ethiopia’s legal landscape pertaining to evictions is framed by several key legislations. Notable among them is the Urban Land Lease Proclamation, which outlines how land can be leased and used for development. This proclamation often serves as a primary legal basis for initiating urban eviction processes.
Additionally, the Housing Development Proclamation aims to facilitate orderly urban expansion by creating a framework for property development. These laws are instrumental in determining the conditions under which evictions may occur. However, critics argue that these legislations sometimes prioritize development over the rights of residents, potentially leading to forced evictions without adequate safeguards.
Assessment of Legal Protections for Residents
While the Ethiopian Constitution guarantees property rights, the actual assessment of legal protections for residents facing eviction reveals a mixed picture. Legal protections for residents often hinge on ownership documentation, which can be lacking due to administrative inefficiencies.
Unfortunately, many residents, especially those in informal settlements, often find themselves inadequately protected by these laws, leading to disputes over land rights during development projects. To address this, there is a growing call for reforms to ensure more comprehensive legal protections for residents and the implementation of fair compensation practices.
International Human Rights Standards
In addition to national laws, international human rights standards play a pivotal role in shaping policies related to evictions. Ethiopia, as a member of the United Nations, is committed to adhering to these standards.
International Laws on Forced Evictions
Internationally, laws on forced evictions are guided by treaties such as the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR), which explicitly calls for the protection against forced evictions. These laws emphasize that evictions should only occur in extreme cases, and with full respect for due process and remedies.
Moreover, the UN Basic Principles and Guidelines on Development-Based Evictions and Displacement provide a framework aimed at ensuring that evictions are carried out in a manner that respects human dignity and offers adequate compensation and resettlement.
Comparative Analysis with Other Nations
Comparing Ethiopia’s practices with those of other nations can provide valuable insights. Countries like South Africa have implemented strong legal frameworks to protect against forced evictions, often regarded as more robust than those in Ethiopia.
For instance, South Africa’s Prevention of Illegal Eviction from and Unlawful Occupation of Land Act (PIE) is frequently cited as a progressive measure that ensures fair judicial oversight before any eviction is carried out. In contrast, Ethiopia’s framework may lack similarly strong oversight and remedial mechanisms, underscoring the need for policy enhancement.
In conclusion, while Ethiopia’s national laws and international commitments establish a basic framework for managing evictions, there is room for significant improvement. Aligning more closely with international standards and incorporating best practices from other nations could provide a more balanced approach to urban development – one that respects both expansion needs and human rights of vulnerable populations.
Impact of Urban Development on Local Communities
Urban development in Ethiopia, while aimed at economic progress and modernization, has brought significant impacts on local communities. Here, we’ll explore the social and economic impacts that have reshaped the lives of thousands.
Social Impacts
Urban development often means displacement for many communities. The social consequences are profound, affecting not just individual lives but entire community dynamics.
Displacement and Its Social Ramifications
Displacement is perhaps the most immediate effect of urban development. As cities expand, many communities are forced to relocate, often without adequate compensation or alternative housing arrangements. This uprooting unsettles social structures and affects the cultural fabric of communities.
- Loss of Community Connections: When families are evicted, they lose more than just a physical space. Traditional support networks like neighbors, local friends, and social groups are disrupted, leading to a sense of isolation.
- Psychological Stress: The uncertainty and upheaval caused by sudden displacement contribute to mental health issues, like anxiety and depression.
- Educational Disruption: Children often suffer breaks in their education, having to switch schools or even drop out if the new location is too far from affordable schools.
Community Responses and Resilience
Despite the challenges, communities often display remarkable resilience. They find innovative ways to cope and adapt to their new circumstances.
- Formation of New Networks: Many displaced families form new community organizations to support each other in unfamiliar environments.
- Advocacy for Rights: Some communities have formed alliances to advocate for better compensation and legal support, often collaborating with NGOs and international bodies.
- Cultural Preservation Efforts: Efforts are made to preserve traditions and cultural practices, even in new environments, through community events and cultural groups.
Economic Impacts
Urban development also has far-reaching economic consequences. While it can open up new job opportunities, it simultaneously threatens the economic stability of existing communities.
Effect on Livelihoods
For many, displacement means losing their primary source of income if their work is tied to their location.
- Loss of Jobs: Artisans, local shop owners, and small farmers often find it difficult to thrive in new areas, losing regular customers and markets.
- Increased Living Costs: Moving to urban centers can lead to higher living expenses, pushing families into poverty.
- Informal Economy Struggles: Those in informal sectors, such as street vending, face difficulties in re-establishing their businesses.
Long-term Economic Considerations
The economic outlook for many displaced communities is uncertain. However, urbanization also presents opportunities for growth if managed inclusively.
- Investment in Skills Development: There’s a need for programs that provide skills training for displaced workers to integrate them into new economic sectors.
- Sustainable Urban Planning: Long-term economic upliftment is possible if urban development includes affordable housing and accommodates the needs of all residents.
- Promotion of Inclusive Growth: Policies that ensure that the benefits of urban growth are shared with displaced communities are crucial for sustainable development.
The impact of urban development on local communities in Ethiopia highlights the urgent need for balanced approaches that consider both growth and the well-being of affected populations.
Source- Amnesty