April 1, 2023
The Habesha
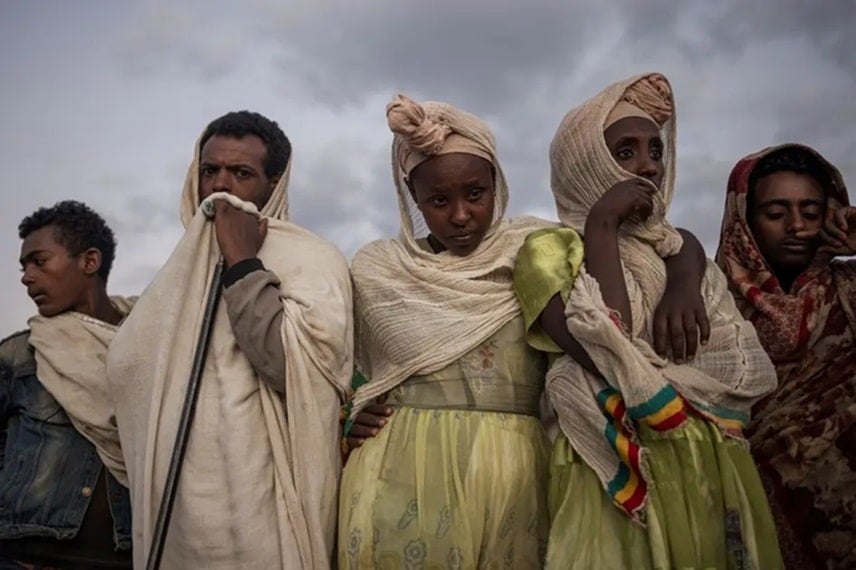
The conflict in the Amhara region of Ethiopia has been a topic of great concern and interest to many around the world. This region, rich in history and culture, has recently faced challenges that have impacted not only local residents but also rippled through the entire nation.
Understanding the roots and the complexities of this conflict helps shed light on the broader socio-political dynamics at play in Ethiopia. Why did the tensions escalate, and what steps are being taken to resolve them?
Join us as we reflect on the ongoing struggles and the hopes for peace in the Amhara region. This exploration provides insights into a conflict that affects the very fabric of Ethiopia.
Historical Context of the Amhara Conflict
Understanding the historical context of the Amhara conflict requires delving into the intricate tapestry of Ethiopia’s ethnic and political landscape. This region, resplendent with a rich history and cultural heritage, has been caught in a web of ethnic tensions and political dynamics that have periodically erupted into conflict.
Origins of Ethnic Tensions
The origins of ethnic tensions in the Amhara region are deeply rooted in the historical relations between various ethnic groups in Ethiopia. Ethnic diversity has been both a source of richness and a flashpoint for conflict, often exacerbated by historical grievances and power disparities.
Historical Relation Between Ethnic Groups
Historical relations between ethnic groups in Ethiopia are complex, with the Amhara often occupying a prominent role in governance and cultural influence. This has sometimes led to friction with other ethnic groups who seek greater autonomy and recognition. Over generations, relations between the Amhara and other ethnicities like the Oromo and Tigrayans have oscillated between collaboration and rivalry, influenced by competing interests and shifting power dynamics.
The Amhara have traditionally been seen as integral in shaping Ethiopia’s national identity and politics, which has occasionally spurred resentment from those who perceive them as dominant.
Colonial and Post-Colonial Impacts
The colonial and post-colonial impacts on Ethiopia have further complicated ethnic relations. Although Ethiopia was never colonized in the traditional sense, the influence of European powers was felt in its political and economic structures. This period saw the imposition of modern state boundaries and centralizing policies that often disregarded existing ethnic territories and identities.
Post-colonial governance continued to grapple with these divisions, as successive regimes struggled to balance ethnic representation with national unity. Policies aimed at ethnic federalism were introduced to address these issues, yet they sometimes deepened divisions, leading to sporadic tensions and violence.
Political Dynamics in Ethiopia
Political dynamics in Ethiopia play a pivotal role in understanding the Amhara conflict. The struggle for power, recognition, and autonomy has been a constant theme in Ethiopia’s political landscape.
Governance and Power Struggles
Governance and power struggles within Ethiopia have revolved around the centralization of authority and the quest for ethnic representation. Historically, Ethiopia was governed through a feudal system that gave certain groups more power. The transition to a more centralized governance structure in the mid-20th century brought both efficiency and conflict, as various ethnic groups, including the Amhara, fought for a stake in political leadership.
The creation of an ethnic federal structure in the 1990s was intended to alleviate these tensions by granting regions more autonomy. However, this move has sometimes intensified power struggles, as ethnic groups vie for resources and political influence within their regions.
Role of Political Parties and Movements
The role of political parties and movements has significantly influenced the Amhara conflict. In recent decades, Ethiopia’s multi-party landscape has been shaped by ethnic-based parties that often emphasize regional interests.
Political movements within the Amhara region have sought greater autonomy and representation, sometimes clashing with national policies. The formation of parties like the Amhara National Democratic Movement highlights the desire for recognition and the complexities inherent in balancing regional aspirations with national unity.
In conclusion, the historical context of the Amhara conflict is a tapestry woven from intricate ethnic relationships, historical grievances, and the evolving political dynamics of Ethiopia. Understanding these elements is crucial in grappling with the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for peace and stability in the region.
Key Events in the Amhara Conflict
The Amhara conflict, deeply rooted in historical, political, and social factors, has been marked by a series of significant events that have shaped its trajectory. This section delves into the key moments that have defined the conflict over time.
Outbreak of Violence
The outbreak of violence in the Amhara region was not an isolated incident but rather a culmination of mounting tensions. The initial outbreaks were characterized by isolated skirmishes that quickly escalated into a broader conflict.
Initial Skirmishes
In the first phases, initial skirmishes erupted in various parts of the Amhara region. These skirmishes often arose from long-standing ethnic tensions and disputes over land and resources. The lack of effective conflict resolution mechanisms contributed to the rapid spread of violence.
Notably, clashes between different ethnic communities highlighted the fragile nature of peace in the area. These early encounters set the stage for larger confrontations, drawing in more actors over time. 🛑 The initial skirmishes were critical as they signaled the beginning of a more extensive struggle impacting the broader region.
Major Milestones in the Conflict
As the conflict progressed, several major milestones defined its course. One such moment was the large-scale mobilization of armed groups, which marked a significant escalation. This period saw an increase in organized and planned attacks that targeted both military and civilian targets.
The involvement of outside actors also influenced the conflict’s dynamics. External support and alliances were formed, further complicating the situation. Each milestone represented a shift in tactics and objectives, making it increasingly challenging to find quick solutions.
Key milestones included significant battles that resulted in heavy casualties and displacement. These turning points underscored the growing humanitarian crisis, drawing international attention to the need for intervention and peacebuilding efforts.
Major Actors Involved
Various major actors have played crucial roles in the Amhara conflict, each contributing unique dynamics to the unfolding narrative.
Local Militias and Forces
Local militias and forces were among the primary actors in the conflict. Many groups formed along ethnic lines, often driven by the perceived need to protect their communities from external threats. These militias were not homogenous and varied significantly in terms of size, capability, and objectives.
Some militias received backing from regional actors, which gave them more legitimacy and resources. The fluid alliances and rivalries among these groups added levels of complexity to the evolving landscape of the conflict. Their activities and the territories they controlled significantly impacted the day-to-day lives of local populations.
Federal and Regional Governments
The roles of the federal and regional governments were central to the conflict’s development. Tensions between these entities often exacerbated local grievances, making it difficult to implement consistent strategies aimed at peace and reconciliation.
The federal government faced challenges in addressing the root causes of the conflict, including ethnic divisions and demands for autonomy. Regional authorities, tasked with maintaining order, struggled with limited resources and competing political interests.
Both levels of government were criticized for failing to prevent the escalation of violence and for not adequately protecting civilians. Their actions and inactions played into the broader narrative of distrust and conflict, highlighting the urgent need for effective governance and conflict resolution mechanisms.
Impact of the Conflict on Local Communities
The Amhara conflict has significantly affected local communities, leaving deep scars on both the social and economic fabric of the region. With each passing day, more stories of personal loss, humanitarian crises, and shattered communities emerge, highlighting the severity of the situation. In this section, we are exploring these impacts in more detail, focusing on humanitarian consequences and the broader economic and social impacts.
Humanitarian Consequences
Displacement and Refugee Crisis
Displacement and the resulting refugee crisis are among the most pressing humanitarian consequences of the Amhara conflict. Thousands of families have been uprooted from their homes, forced to flee in search of safety and shelter. Refugee camps are overflowing as neighboring regions and countries grapple with the influx of displaced persons.
This surge not only strains resources but also tests the capacity of humanitarian organizations to provide adequate support.
This crisis leads to:
- A large number of internally displaced people (IDPs).
- Overcrowded refugee camps in Ethiopia and neighboring countries.
- Scarcity of basic necessities such as food, water, and medical supplies.
The emotional and physical toll on those displaced is immense, as individuals and families are forced into precarious living conditions with limited access to essential services.
Human Rights Violations
Human rights violations have been an unfortunate hallmark of the Amhara conflict. Numerous reports of abuses underscore the dire need for international attention and immediate intervention. Such violations include:
- Cases of arbitrary arrests and detentions.
- Instances of torture and inhumane treatment.
- Reports of sexual violence.
In many instances, the victims are left with little to no legal recourse, and perpetrators often go unpunished, further eroding trust in local and national governance systems.
Economic and Social Impacts
Infrastructure and Livelihood Disruptions
Infrastructure and livelihood disruptions are another devastating outcome of the conflict. Essential infrastructures such as roads, schools, and hospitals have been damaged or destroyed, crippling daily life and economic activities in the region.
Many communities find themselves without the means to rebuild, trapping them in a cycle of poverty and stagnation.
Key impacts include:
- Destruction of roads disrupting trade and movement.
- Educational institutions being inoperable, affecting the future of countless children.
- Collapse of local businesses, leading to widespread unemployment.
These disruptions have a long-term effect on the region’s development prospects, making recovery efforts all the more challenging.
Social Cohesion and Community Relations
The conflict has severely strained social cohesion and community relations in the Amhara region. Trust between different ethnic groups and within communities has been eroded, often leading to increased tension and suspicion.
Community relations suffer from:
- Deepening ethnic divides and prejudices.
- Loss of communal support networks.
- Increased incidents of local conflicts and violence.
Restoring these damaged relationships is a daunting task that requires focused effort and time. It is crucial for peace-building initiatives to prioritize reconciliation and the rebuilding of trust among the communities to foster a harmonious coexistence.
In conclusion, addressing the multifaceted impacts of the Amhara conflict on local communities requires holistic approaches combining humanitarian aid, economic support, and community reconciliation efforts. Without such comprehensive intervention, the journey towards recovery and peace remains an uphill battle.
Current Status and Efforts for Peace
In the wake of the tumultuous conflict in the Amhara region of Ethiopia, various peace initiatives and dialogues have been set in motion to address the ongoing challenges. The current situation is delicate, with significant efforts required from both local and international actors to forge a path towards lasting peace.
Peace Initiatives and Dialogues
Efforts to calm tensions and promote peace in the Amhara region have seen multi-faceted approaches with dialogues being a key strategy. These dialogues aim at addressing the root causes of the conflict and establishing mutual understanding among the involved parties.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations have played a pivotal role in facilitating dialogues and frameworks for peace. Bodies such as the United Nations and the African Union have been instrumental in mediating discussions between conflicting parties. By providing neutral ground, they help ensure that conversations remain focused on constructing paths toward reconciliation. Furthermore, international organizations often extend humanitarian aid to mitigate the repercussions of the conflict on local populations, aiding in stability recovery.
Local and National Peace Efforts
Locally, community leaders and religious figures are taking initiative by engaging directly with affected communities to foster understanding and empathy across ethnic borders. The Ethiopian government has initiated various peace talks, inviting representatives from all sides, including opposition groups, to negotiate an inclusive peace plan. Such efforts aim to create national unity and reduce hostility, paving the way for permanent peaceful coexistence.
Challenges to Resolving the Conflict
While efforts for peace are underway, several significant challenges persist that complicate the peace process.
Political and Ethnic Obstacles
Political dynamics within Ethiopia present considerable obstacles. Competing interests among ethnic groups and political leaders often result in stalled negotiations. Ethnic tensions have historically led to deep mistrust, making cooperation difficult. Navigating the complex political landscape requires careful negotiation and compromise, as well as strong leadership capable of drawing factions together.
Sustainability of Proposed Solutions
Sustainability remains a critical concern. Many proposed solutions encounter challenges in feasibility and implementation, especially when addressing entrenched issues like resource distribution, displacement, and infrastructure development. Ensuring that peace initiatives are inclusive and adaptable to dynamic socio-political changes is essential for their endurance. Continuous engagement and monitoring are vital to ensure the solutions achieve the intended outcomes and are resilient to potential disruptions.
Reflections and Lessons Learned
Reflecting on the conflict in the Amhara region, it is important to draw valuable lessons to better understand such complex situations and to pave the way forward. The insights gained from these tumultuous events not only shed light on the nature of ethnic conflicts but also on the broader implications for regional stability.
Insights from the Conflict
Understanding Ethnic Conflicts
Understanding ethnic conflicts requires delving into the historical, social, and political fabric of a region. In the Amhara region, as in many parts of Ethiopia, ethnic identity plays a crucial role in community interactions and governance structures. These identities, while a source of cultural richness, can also become points of tension when aligned with political power struggles.
A key lesson is the importance of ethnic inclusivity and dialogue in governance. Conflicts are often fueled by perceptions of marginalization or exclusion, leading to grievances that can erupt into violence. Recognizing these signs early and addressing them through inclusive policies is essential.
Implications for Regional Stability
The implications for regional stability are profound. When conflict erupts in one area, it often reverberates across borders, affecting neighboring regions and countries. This instability can lead to humanitarian crises such as mass displacements and strain on infrastructure, which are costly and challenging to manage.
Moreover, the economic ripple effects of instability are significant. Trade routes can be disrupted, local businesses can suffer, and investment in the region can decline. Thus, fostering peace and stability in regions like Amhara is not only crucial for local communities but also for broader regional security and economic health.
Future Directions for Amhara Region
Long-term Peacebuilding Strategies
For lasting peace in the Amhara region, a focus on long-term peacebuilding strategies is critical. These strategies can involve:
- Reconciliation programs that aim to repair community relations.
- Economic development initiatives to tackle the root causes of conflict, such as poverty and unemployment.
- Educational programs that promote tolerance and understanding across ethnic lines.
It is essential to create an environment where dialogue and negotiation are the primary means of resolving disputes, and where the benefits of peace are visible and tangible for everyone.
Role of Community Involvement
The role of community involvement cannot be overstated. Local communities are the backbone of any peace process. Engaging community leaders, civil society groups, and local institutions in peacebuilding endeavors ensures that initiatives are grounded in the realities and needs of those directly affected by the conflict.
By empowering communities to take an active role in peace efforts, it is possible to build resilience against future conflicts. Local ownership of peace processes also contributes to sustainable peace, as solutions are more likely to be respected and upheld by the people they impact the most.
Drawing lessons from the Amhara conflict, the journey towards peace and stability begins with acknowledging the complex interplay of ethnic, cultural, and political factors. Efforts must focus not only on addressing immediate tensions but also on laying the groundwork for a peaceful future.