(HRW) — Ethiopia is on a deteriorating human rights trajectory as parliamentary elections approach in 2010. These will be the first national elections since 2005, when post-election protests resulted in the deaths of at least 200 protesters, many of them victims of excessive use of force by the police. Broad patterns of government repression have prevented the emergence of organized opposition in most of the country. In December 2008 the government re-imprisoned opposition leader Birtukan Midekssa for life after she made remarks that allegedly violated the terms of an earlier pardon.
In 2009 the government passed two pieces of legislation that codify some of the worst aspects of the slide towards deeper repression and political intolerance. A civil society law passed in January is one of the most restrictive of its kind, and its provisions will make most independent human rights work impossible. A new counterterrorism law passed in July permits the government and security forces to prosecute political protesters and non-violent expressions of dissent as acts of terrorism.
Political Repression and the 2010 Elections
As Ethiopia heads toward nationwide elections, the government continues to clamp down on the already limited space for dissent or independent political activity. Ordinary citizens who criticize government policies or officials frequently face arrest on trumped-up accusations of belonging to illegal “anti-peace” groups, including armed opposition movements. Officials sometimes bring criminal cases in a manner that appears to selectively target government critics, as when in June 2009 prominent human rights activist Abebe Worke was charged with illegal importation of radio equipment and ultimately fled the country. In the countryside government-supplied (and donor-funded) agricultural assistance and other resources are often used as leverage to punish and prevent dissent, or to compel individuals into joining the ruling party.
The opposition is in disarray, but the government has shown little willingness to tolerate potential challengers. In December 2008 the security forces re-arrested Birtukan Midekssa, leader of the Unity for Democracy and Justice Party, which had begun to build a grassroots following in the capital. The government announced that Birtukan would be jailed for life because she had made public remarks that violated the terms of an earlier pardon for alleged acts of treason surrounding the 2005 elections. The authorities stated that there was no need for a trial as the move was a mere legal technicality.
In July the Ethiopian government passed a new anti-terrorism law. The law provides broad powers to the police, and harsh criminal penalties can be applied to political protesters and others who engage in acts of nonviolent political dissent. Some of its provisions appear tailored less toward addressing terrorism and more toward allowing for a heavy-handed response to mass public unrest, like that which followed Ethiopia’s 2005 elections.
Civil Society Activism and Media Freedom
The space for independent civil society activity in Ethiopia, already extremely narrow, shrank dramatically in 2009. In January the government passed a new civil society law whose provisions are among the most restrictive of any comparable law anywhere in the world. The law makes any work that touches on human rights or governance issues illegal if carried out by foreign non-governmental organizations, and labels any Ethiopian organization that receives more than 10 percent of its funding from sources outside of Ethiopia as “foreign.” The law makes most independent human rights work virtually impossible, and human rights work deemed illegal under the law is punishable as a criminal offense.
Ethiopia passed a new media law in 2008 that improved upon several repressive aspects of the previous legal regime. The space for independent media activity in Ethiopia remains severely constrained, however. In August two journalists were jailed on charges derived partly from Ethiopia’s old, and now defunct, press proclamation. Ethiopia’s new anti-terror law contains provisions that will impact the media by making journalists and editors potential accomplices in acts of terrorism if they publish statements seen as encouraging or supporting terrorist acts, or even, simply, political protest.
Pretrial Detention and Torture
The Ethiopian government continues its longstanding practice of using lengthy periods of pretrial and pre-charge detention to punish critics and opposition activists, even where no criminal charges are ultimately pursued. Numerous prominent ethnic Oromo Ethiopians have been detained in recent years on charges of providing support to the outlawed Oromo Liberation Front (OLF); in almost none of these cases have charges been pursued, but the accused, including opposition activists, have remained in detention for long periods. Canadian national Bashir Makhtal was convicted on charges of supporting the rebel Ogaden National Liberation Front (ONLF) in July, after a trial that was widely criticized as unfair; he was in detention for two-and-a-half years before his sentence was handed down, and he was unable to access legal counsel and consular representatives for much of that period.
Not only are periods of pretrial detention punitively long, but detainees and convicted prisoners alike face torture and other ill-treatment. Human Rights Watch and other organizations have documented consistent patterns of torture in police and military custody for many years. The Ethiopian government regularly responds that these abuses do not exist, but even the government’s own Human Rights Commission acknowledged in its 2009 annual report that torture and other abuses had taken place in several detention facilities, including in Ambo and Nekemte.
Impunity for Military Abuses
The Ethiopian National Defense Force (ENDF) has committed serious abuses, in some cases amounting to war crimes or crimes against humanity, in several different conflicts in recent years. Human Rights Watch is not aware of any meaningful efforts to hold the officers or government officials most responsible for those abuses to account. The only government response to crimes against humanity and other serious abuses committed by the military during a brutal counterinsurgency campaign in Gambella in late 2003 and 2004 was an inquiry that prosecuted a handful of junior personnel for deliberate and widespread patterns of abuse. No one has been investigated or held to account for war crimes and other widespread violations of the laws of war during Ethiopia’s bloody military intervention in neighboring Somalia from 2006 to 2008.
In August 2008 the Ethiopian government did purport to launch an inquiry into allegations of serious crimes in Somali Regional State, where the armed forces have been fighting a campaign against the rebel Ogaden National Liberation Front for many years. The inquiry was sponsored by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, lacked independence, and concluded that no serious abuses took place. To date the government continues to restrict access of independent investigators into the area.
Relations in the Horn of Africa
In August the Eritrea-Ethiopia Claims Commission issued its final rulings on monetary damages stemming from the bloody 1998-2000 border war between Ethiopia and Eritrea. Nonetheless the two countries remain locked in an intractable dispute about the demarcation of the heavily militarized frontier. Eritrea continues to play a destabilizing role throughout the Horn of Africa through its efforts to undermine and attack the government of Ethiopia wherever possible. The government of President Isayas Afewerki hosts and materially supports fighters from Ethiopian rebel movements, including the Oromo Liberation Front. Eritrea has also pursued a policy of supporting armed opposition groups in Somalia as a way of undermining Ethiopia’s support for the country’s weak Transitional Federal Government.
Key International Actors
Ethiopia is one of the most aid-dependant countries in the world and received more than US$2 billion in 2009, but its major donors have been unwilling to confront the government over its worsening human rights record. Even as the country slides deeper into repression, the Ethiopian government uses development aid funding as leverage against the donors who provide it-many donors fear that the government would discontinue or scale back their aid programs should they speak out on human rights concerns. This trend is perhaps best exemplified by the United Kingdom, whose government has consistently chosen to remain silent in order to protect its annual £130 million worth of bilateral aid and development programs.
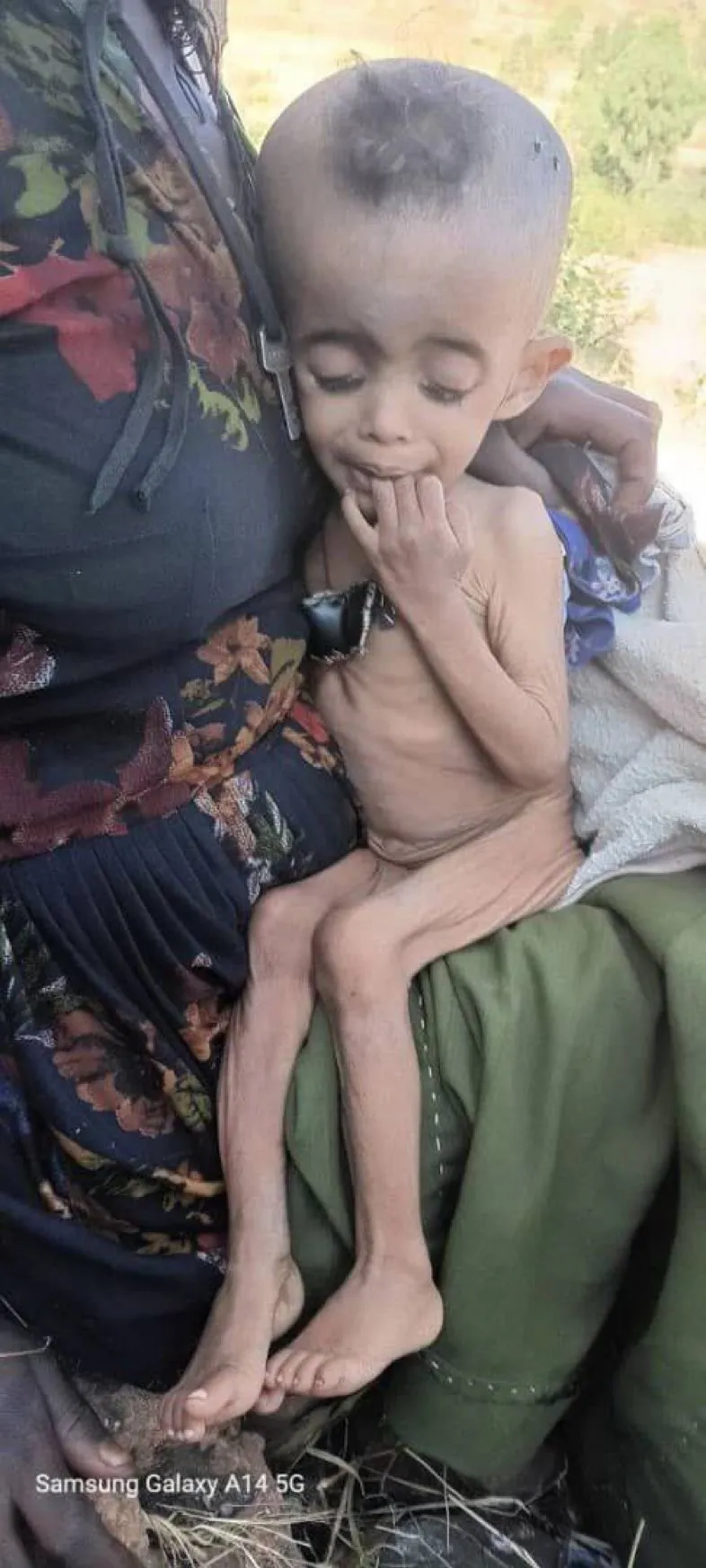
Donors are also fearful of jeopardizing access for humanitarian organizations to respond to the drought and worsening food crisis. Millions of Ethiopians depend on food aid, and the government has sought to minimize the scale of the crisis and restrict access for independent surveys and response.
While Ethiopia’s government puts in place measures to control the elections in 2010, many donors have ignored the larger trends and focused instead on negotiating with the government to allow them to send election observers.
A significant shift in donor policy toward Ethiopia would likely have to be led by the US government, Ethiopia’s largest donor and most important political ally on the world stage. But President Barack Obama’s administration has yet to depart from the policies of the Bush administration, which consistently refused to speak out against abuses in Ethiopia. While the reasons may be different-the current government is not as narrowly focused on security cooperation with Ethiopia as was the Bush administration- thus far the practical results have been the same. The events described above attracted little public protest from the US government in 2009.